We run our stack on ElasticBeanStalk - and have potentially large payloads. The default payload length is 1MB for nginx - which was too small for us. Here’s how to update that in ElasticBeanStalk if you run a Dockerfile.
The problem boils down to the runtime configuration of the docker file is not modifiable within the Dockerfile - you have to modify it using ElasticBeanStalk’s deployment method - YOU CANNOT MODIFY YOUR NGINX FROM WITHIN YOUR DOCKERFILE (unless you’re doing docker-compose.)
Unfortunately - AWS’s documentation is pretty poor here.
The solution
This works for the new AWS Linux 2 environment. To fix this - you need to wrap your configuration file. You should have, if you’re using Docker, a zip file (mine is called deploy.zip) that contains your Dockerrun.aws.json. If you don’t - it’s rather easy to modify, just zip your deploy via
zip -r deploy.zip Dockerrun.aws.json
With that - you now need to add a .platform folder as follows:
APP ROOT
├── Dockerfile
├── Dockerrun.aws.json
├── .platform
│ └── nginx
│ └── conf.d
│ └── custom.conf
You can name your custom.conf whatever you want, and can have as many files as you want. Inside custom.conf, you simply need to place the following inside
client_max_body_size 50M;
Or whatever you want for your config. With that - modify your zip to now be
zip -r deploy.zip Dockerrun.aws.json .platform
And deploy. Your Nginx server will now respect the new command
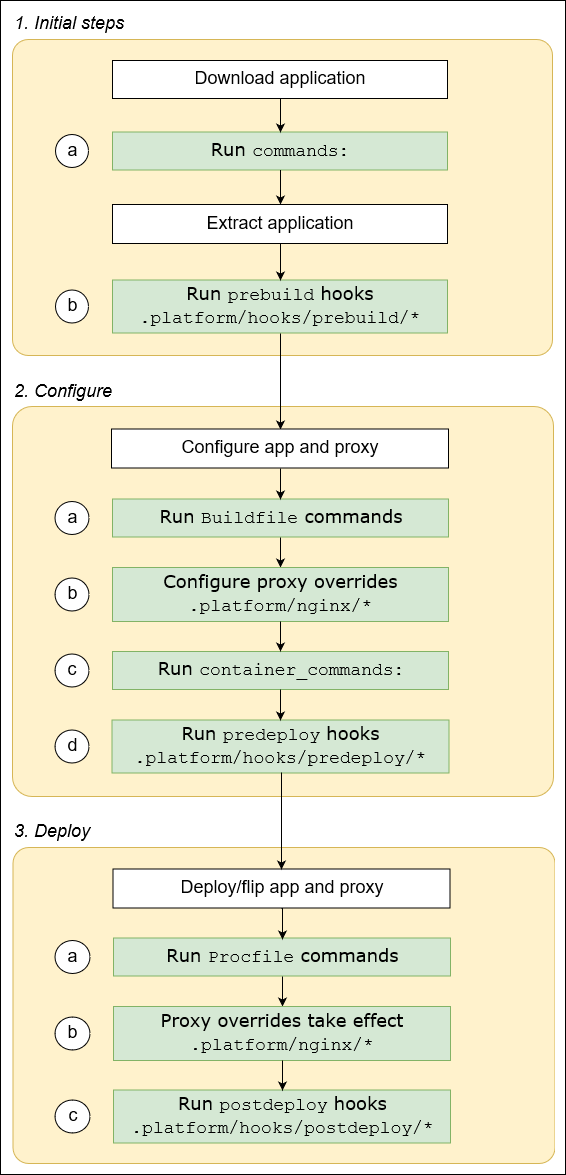
Why this works
This comes from AWS’ documentation - note how in the steps of how Elastic Bean Stalk builds your application - there’s an explicit step to run your hooks & nginx config under the .platform - we’re simply providing that information.
Thanks to https://blog.cyplo.dev/posts/2018/04/beanstalk-docker-environment-variables/ for the inspiration.
